A Shock Wave is an acoustic wave characterized by fluctuations in pressure and density.
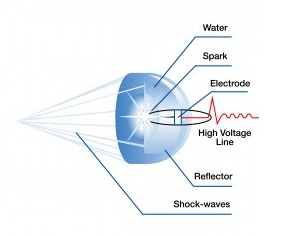 Shock wave technology is used to generate extracorporeal (meaning outside of the body) acoustic waves to non-invasively treat specific sites deep within the body tissue. These waves are generated by an underwater high-voltage spark, which create single pulse waves with high-pressure amplitude, small pulse width, and short rise time.
Shock wave technology is used to generate extracorporeal (meaning outside of the body) acoustic waves to non-invasively treat specific sites deep within the body tissue. These waves are generated by an underwater high-voltage spark, which create single pulse waves with high-pressure amplitude, small pulse width, and short rise time.
Medispec’s patented probe deigns use special ellipsoid reflectors that bounce the shock waves between two focal points, focusing the energy on the affected area.. These shock waves travel through fluid and soft tissue where a change in impedance results in the release of kinetic energy. Studies have demonstrated that shock waves induce an inflammatory response and neovascularization of the affected area– relieving pain, improving blood flow, and ultimately resulting in tissue regeneration and repair.
![]() International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment ISMST
International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment ISMST
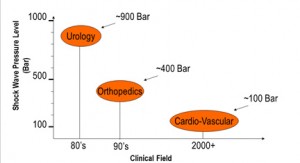 Extracorporeal shock waves were introduced to the medical industry approximately 20 years ago to disintegrate kidney stones and since this time shock waves have changed the treatment of urolithiasis substantially. Today shock waves are the first choice to treat kidney and ureteral stones.
Extracorporeal shock waves were introduced to the medical industry approximately 20 years ago to disintegrate kidney stones and since this time shock waves have changed the treatment of urolithiasis substantially. Today shock waves are the first choice to treat kidney and ureteral stones.
Urology is not the only medical field for shock waves in medicine: Shock waves have been used in Orthopedics and Traumatology to treat insertion tendinitis, non- or delayed unions, avascular necrosis and various necrotic bone alterations. Another field of shock wave application is the treatment of tendons, ligaments and bones on horses in veterinary medicine. The idea of the shock wave therapy for orthopedic diseases is the stimulation of the healing processes in tendons, surrounding tissue and bones.
![]() International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment ISMST
International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment ISMST
Electrohydraulic
Spark Gap technology: the shock waves are generated under water using an electrode placed in an ellipsoid reflector.The energy produced from the spark discharge is reflected and concentrated at a second focal point (F2)
Electromagnetic
When electricity is applied to the coil, the metallicmembrane is repelled to the opposing magnetic field, creating shock waves. The shock waves are transmitted to the focal point by an acoustic lens or a parabolic reflector.
Piezoelectric / Sphere
Ceramic elements are lined on a reflector dish. As these elements are activated by high-voltage electric currents they generate shock waves in a fluid medium. These shock waves are reflected off the reflector dish and are localized to a focal point.
